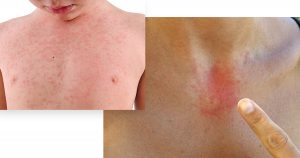
A Look at Contact Dermatitis with Advanced Dermatology, PC
Contact dermatitis is a skin condition that many of us have encountered at some point in our lives. It occurs when the skin encounters substances that trigger an allergic reaction or irritation, leading to various symptoms and discomfort.
Whether it’s a sudden rash after wearing a new piece of jewelry or redness from exposure to certain chemicals, contact dermatitis is a prevalent concern.
The most common types of this skin condition are:
- Contact dermatitis on the face
- Contact dermatitis on the eyelid
- Contact dermatitis on the hands
This condition can be divided into two main types: allergic contact dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis, each with its unique triggers and characteristics.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the intricacies of contact dermatitis, helping you understand what it is, its common causes, and how it manifests on the skin. We’ll also discuss the significance of accurate diagnosis and available treatment options, aiming to provide comprehensive insights to better grasp this dermatological issue.
Continue reading to learn more.
Contact Dermatitis Symptoms and Causes
Contact dermatitis often makes its presence known through mildly irritating to distressing symptoms. These symptoms serve as red flags, alerting us to potential triggers our skin has come into contact with.
Common contact dermatitis symptoms include:
- Redness
- Itching
- Swelling
- Blisters
Common triggers include:
- Nickel and other metals found in jewelry, belt buckles, or clothing snaps
- Fragrances in perfumes, colognes, lotions, and skincare products
- Makeup, skincare products, and nail polish
- Latex in items like rubber gloves, condoms, and some medical devices
- Plants such as poison ivy, oak, and sumac
- Some topical medications, such as antibiotic ointments or corticosteroids
- Various chemicals in cleaning products, solvents, and other substances
These triggers and symptoms can vary from person to person. What causes a reaction in one individual may not affect another. Accurate diagnosis and understanding your triggers are key to effective management and prevention.

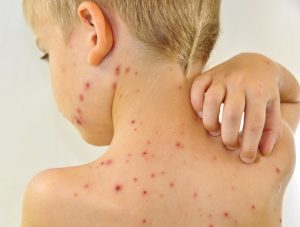
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis is a medical skin condition triggered by specific allergens.
It begins with exposure to substances containing these allergens, such as metals, fragrances, cosmetics, latex, plants, medications, and chemicals.
During the initial exposure, your immune system recognizes the allergen as a threat, leading to sensitization and the creation of memory cells.
Upon repeat exposure to the same allergen, your immune system releases chemicals like histamines, causing skin symptoms like redness, itching, swelling, and sometimes blisters.
Symptoms typically appear hours to a couple of days after exposure. Removing the allergen allows the skin to heal, but re-exposure can lead to a cycle of dermatitis. Managing symptoms, identifying allergens, and prevention are vital for care.
Irritant Contact Dermatitis
Irritant contact dermatitis is a skin condition resulting from exposure to irritating substances rather than allergens.
It occurs when the skin’s natural protective barrier is damaged due to contact with harsh chemicals, solvents, or physical irritants like friction and excessive moisture.
Unlike allergic contact dermatitis, irritant contact dermatitis does not involve the immune system’s sensitization process.
Symptoms of irritant contact dermatitis include redness, dryness, itching, burning, and sometimes blistering.
Unlike the delayed reaction in allergic contact dermatitis, these symptoms often appear within a few hours after exposure.
The critical difference is that irritant contact dermatitis can affect anyone, regardless of previous exposure. In contrast, allergic contact dermatitis develops only in individuals who have become sensitized to a particular allergen over time.
Diagnosis and Testing for Contact Dermatitis
Diagnosing contact dermatitis involves clinical assessment and testing to identify the specific allergen or irritant causing the skin reaction.
A dermatologist begins by taking a detailed medical history, including information about recent exposure to potential allergens or irritants. They may inquire about personal and family history of skin conditions or allergies.
A thorough physical examination is conducted to assess the affected skin. The dermatologist examines the rash, blisters, redness, and other symptoms to determine the type and severity of the dermatitis.
Patch testing is a common method to diagnose allergic contact dermatitis. During this test, small quantities of potential allergens are applied to adhesive patches, which are then placed on the patient’s skin, typically on the back. The patches remain in place for 48 hours, and then the patient returns for an evaluation. Any skin reactions observed can help identify the specific allergens responsible.
Skin prick tests are another way to diagnose allergic contact dermatitis. In this test, a diluted allergen solution is applied to the skin, and the dermatologist uses a small lancet to create a tiny prick or scratch on the skin’s surface. Any immediate skin reactions are monitored to identify allergens.
Sometimes, blood tests may be conducted to identify allergic reactions by measuring specific antibodies or immune responses to potential allergens. However, patch testing is often the preferred method for contact dermatitis diagnosis.
An elimination diet may be recommended for dermatitis related to food allergies to identify specific food triggers.
In rare cases, a skin biopsy may rule out other skin conditions or examine the extent of skin damage.
Contact Dermatitis Treatment
Contact dermatitis treatments focus on managing and alleviating symptoms caused by skin reactions. The approach to treatment can vary depending on the type and severity of the dermatitis.
Some common treatment options include:
- Topical or oral corticosteroids
- Immuno-modulators like tacrolimus (Protopic) and pimecrolimus (Elidel)
- Oral antihistamines like cetirizine (Zyrtec) and loratadine (Claritin)
- Moisturizers and emollients
- Trigger avoidance
- Cool compresses
- Antibiotics
It’s essential to consult a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the type of contact dermatitis and its severity, which may include contact dermatitis medication.
Understanding Contact Dermatitis Healing Stages
The healing process of contact dermatitis typically unfolds in several stages as the skin repairs itself from the damage caused by allergens or irritants.
These stages may vary in duration and intensity based on the severity of the dermatitis, individual factors, and the effectiveness of treatment.
Here’s an overview of the stages of healing for contact dermatitis:
Inflammatory Stage
This initial phase of contact dermatitis is characterized by redness, itching, and inflammation of the affected skin. Inflammation occurs as a response to the irritating substance, and it’s the body’s way of attempting to eliminate or neutralize the threat. This stage may last from hours to several days, depending on the severity of the reaction and the effectiveness of early treatment.
Vesicular Stage
Small blisters may develop in the affected area, particularly with allergic contact dermatitis. These blisters are filled with fluid and can be intensely itchy. They are a sign of deeper skin involvement. This stage may last for several days.
Exudative Stage
During this stage, the blisters may rupture, releasing fluid. The skin may also ooze clear or yellowish discharge, and crusting may occur as the skin dries. This stage may overlap with the vesicular stage and last a few days.
Resolution Stage
As the inflammatory process subsides, the skin starts to heal. Itchiness and redness gradually diminish, and the skin returns to its normal appearance.
The duration of this stage can vary widely, from several days to weeks.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
After the dermatitis heals, some individuals may experience darkening of the skin in the affected area, known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). PIH can take weeks or months to resolve but often fades over time. Proper sun protection and the use of skin-lightening agents may help manage PIH.
Complete Healing
Eventually, the skin fully recovers and returns to its pre-dermatitis condition. How long this stage takes can vary depending on factors such as the type of dermatitis, the effectiveness of treatment, and individual healing rates.
It’s important to note that early treatment, avoiding trigger substances, and the individual’s overall health can influence healing stages.
Sometimes, the skin may become lighter than the surrounding skin after contact dermatitis heals. This hypo-pigmentation can persist for weeks or months before returning to normal skin tone.
FAQ About Contact Dermatitis
How do you cure contact dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is caused by a foreign substance or object that comes in contact with your skin. The exact remedy will vary depending on the substance or object, the area that was affected, and the patient’s skin type, among other factors.
What does contact dermatitis look like?
This skin condition looks like a red rash that may, in some instances, have a rough texture. It can appear in most parts of the body.
What is the first sign of contact dermatitis?
The first sign of contact dermatitis is an itchy, numb, or uncomfortable sensation in the area exposed to the irritant.
Can contact dermatitis be caused by stress?
Unlike eczema and other dermatitis symptoms, contact dermatitis cannot be caused by stress. This condition is only caused by external elements that encounter your skin, producing an unwanted reaction.
Is contact dermatitis contagious?
No, Contact dermatitis is not contagious. It is not caused by an infectious agent like bacteria or viruses. Instead, it occurs when the skin reacts to an irritant or allergen, and it is not transmitted from person to person through direct contact.
Can contact dermatitis spread?
Not usually. Contact dermatitis typically doesn’t spread from one area of the body to another through contact with the affected skin. However, if exposure to the irritant or allergen continues, the condition may worsen or persist throughout the body.
When should I see a doctor for contact dermatitis?
If the rash appears suddenly, is extremely uncomfortable, or affects your daily life, you should see a skincare expert who can identify the potential source and offer a solution to soothe the discomfort.
Get Treatment for Your Contact Dermatitis Rash Now
Are you or a loved one living with itching, burning, or a rash due to contact dermatitis? Our team at Advanced Dermatology, PC, is here to help.
Offering state-of-the-art diagnosis and treatment options in various locations throughout the tri-state area, you can find the relief you need sooner with us.
